Introduction
Sinharaja Forest Reserve is a stunning and ecologically diverse tropical rainforest located in the southwestern part of Sri Lanka. This majestic forest, recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is renowned for its rich biodiversity, pristine beauty, and significant conservation value. In this article, we will explore the wonders of Sinharaja Forest Reserve, diving into its natural treasures, importance, and efforts to preserve this invaluable ecosystem.



Table of Contents
- What is Sinharaja Forest Reserve?
- Geographical Location
- Flora and Fauna
- Importance of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
- Conservation Efforts
- Visiting Sinharaja Forest Reserve
- Guidelines for Visitors
- Threats and Challenges
- Research and Education
- Impacts of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
- The Future of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. What is Sinharaja Forest Reserve?
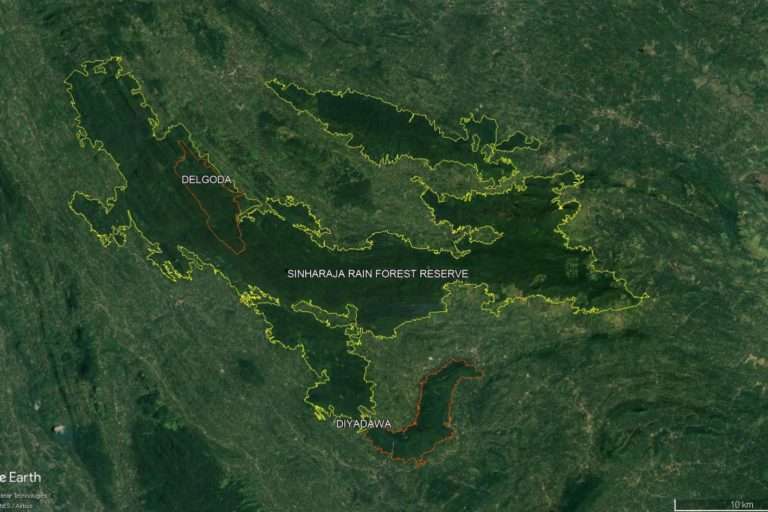
Sinharaja Forest Reserve is a pristine tropical rainforest spanning approximately 11,187 hectares. It is one of the few remaining lowland rainforests in Sri Lanka, offering a sanctuary for numerous plant and animal species. The name “Sinharaja” translates to “Lion Kingdom” in Sinhalese, symbolizing the regal nature of this forest.
2. Geographical Location
Situated in the southwestern part of Sri Lanka, Sinharaja Forest Reserve is nestled between the districts of Ratnapura, Galle, and Matara. It is located within the Sabaragamuwa and Southern provinces, making it easily accessible from various parts of the country.
3. Flora and Fauna
Sinharaja Forest Reserve is a treasure trove of biodiversity, boasting an impressive array of flora and fauna. The forest is home to over 830 plant species, including numerous endemic and endangered ones. Towering trees such as Dipterocarpus, Mesua, and Dillenia form the majestic canopy of Sinharaja, creating a dense and vibrant ecosystem.
In terms of fauna, Sinharaja is equally awe-inspiring. The forest is inhabited by a diverse range of animal species, including 44 species of mammals, 160 species of birds, 33 species of reptiles, and 15 species of amphibians. Notable wildlife found in the reserve includes the purple-faced langur, Sri Lankan leopard, and the endemic Sri Lankan blue magpie.





















4. Importance of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
Sinharaja Forest Reserve holds immense ecological, cultural, and scientific importance. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, it has been recognized for its outstanding universal value. The forest acts as a vital watershed, contributing to the water supply of numerous rivers and streams in the region. It also plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by acting as a carbon sink.
From a cultural perspective, Sinharaja is deeply ingrained in Sri Lanka’s heritage. It has spiritual significance and is associated with ancient rituals and beliefs. The forest serves as a living laboratory for scientists and researchers, offering valuable insights into evolutionary processes, endemic species, and ecological dynamics.



5. Conservation Efforts
Preserving the fragile ecosystem of Sinharaja Forest Reserve has been a top priority for the Sri Lankan government and various conservation organizations. Strict regulations are in place to protect the forest from human encroachment, illegal logging, and poaching. The Forest Department and other entities work tirelessly to enforce these regulations and raise awareness about the importance of conservation.
Collaborative efforts between local communities, researchers, and conservationists have resulted in successful projects aimed at reforestation, wildlife monitoring, and sustainable tourism initiatives. These endeavors strive to strike a balance between the needs of local communities and the long-term preservation of the forest.
6. Visiting Sinharaja Forest Reserve
Sinharaja Forest Reserve offers a remarkable opportunity for nature enthusiasts and adventurers to immerse themselves in its unparalleled beauty. The forest provides various trails and trekking routes, allowing visitors to explore its wonders while being guided by experienced naturalists.



7. Guidelines for Visitors
To ensure the conservation of Sinharaja Forest Reserve, it is essential for visitors to adhere to certain guidelines. These guidelines include:
- Obtaining necessary permits and following the designated trails.
- Avoiding littering and disposing of waste responsibly.
- Respecting the flora and fauna by not plucking plants or disturbing animals.
- Refraining from making excessive noise to maintain the serene environment.
- Following the guidance of experienced guides and naturalists.
8. Threats and Challenges
Despite the conservation efforts, Sinharaja Forest Reserve faces various threats and challenges. The encroachment of human settlements, illegal logging, and poaching pose significant risks to the delicate balance of this ecosystem. Climate change, invasive species, and habitat fragmentation further exacerbate the challenges faced by the forest.
9. Research and Education
Research and education play crucial roles in understanding and preserving the unique ecosystem of Sinharaja Forest Reserve. Scientists and researchers conduct studies on various aspects of the forest, contributing to our knowledge of biodiversity, ecological processes, and conservation strategies. Educational programs and awareness campaigns help instill a sense of responsibility and stewardship among the local communities and visitors.
10. Impacts of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
The preservation of Sinharaja Forest Reserve has far-reaching impacts. The forest acts as a natural haven for biodiversity, ensuring the survival of numerous endemic and endangered species. It also supports the livelihoods of local communities through sustainable tourism, providing economic opportunities while safeguarding the forest’s integrity.
Furthermore, Sinharaja Forest Reserve contributes to global efforts in combating climate change by sequestering carbon and maintaining vital ecosystem services. Its preservation serves as a testament to the importance of safeguarding our planet’s natural heritage.
11. The Future of Sinharaja Forest Reserve
The future of Sinharaja Forest Reserve lies in our hands. It requires continued dedication, collaborative efforts, and sustainable practices to ensure its survival for future generations. Strengthening conservation measures, promoting research and education, and fostering community engagement are crucial steps towards securing the future of this remarkable rainforest.
Conclusion
Sinharaja Forest Reserve stands as a remarkable testament to the beauty and significance of tropical rainforests. Its rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and conservation efforts make it a jewel among UNESCO World Heritage Sites. By embracing sustainable practices and preserving this natural treasure, we can contribute to the protection of our planet’s invaluable ecosystems.
FAQs
1. Are there accommodation options available near Sinharaja Forest Reserve? Yes, there are several accommodation options available near Sinharaja Forest Reserve, ranging from eco-lodges to guesthouses. It is advisable to make prior arrangements and book accommodations in advance.
2. Can I visit Sinharaja Forest Reserve without a guide? No, visiting Sinharaja Forest Reserve without a guide is not allowed. The expertise of experienced guides is essential to ensure a safe and informative visit while minimizing the impact on the ecosystem.
3. Are there any restrictions on photography within the reserve? Photography is allowed in Sinharaja Forest Reserve, but it is important to be mindful of the environment and respect the guidelines provided by the authorities. Avoid using flash photography, as it can disturb wildlife.
4. Can I swim in the rivers or waterfalls within Sinharaja Forest Reserve? Swimming in the rivers or waterfalls within Sinharaja Forest Reserve is generally not permitted for safety reasons. However, there are designated areas nearby where visitors can enjoy water activities.
5. How can I contribute to the conservation of Sinharaja Forest Reserve? You can contribute to the conservation of Sinharaja Forest Reserve by supporting sustainable tourism practices, respecting the guidelines, spreading awareness about its importance, and supporting local conservation organizations through donations or volunteer work.


